How a Mining Pool Works: The Technology of Distributed Mining
A mining pool represents a collaborative activity of a group of miners who combine their computing resources to increase the likelihood of successfully solving cryptographic tasks faced by blockchain networks such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others. This process is crucial as it is directly linked to the support and security of blockchain networks and transaction processing. Mining pools make mining more accessible and economically viable for individual participants.
Earn more money with Headframe
Получите лучшую доходность в майнинге. Самая низкая на рынке комиссия 0.9%, обход блокировок и ежедневные бесплатные выплаты.
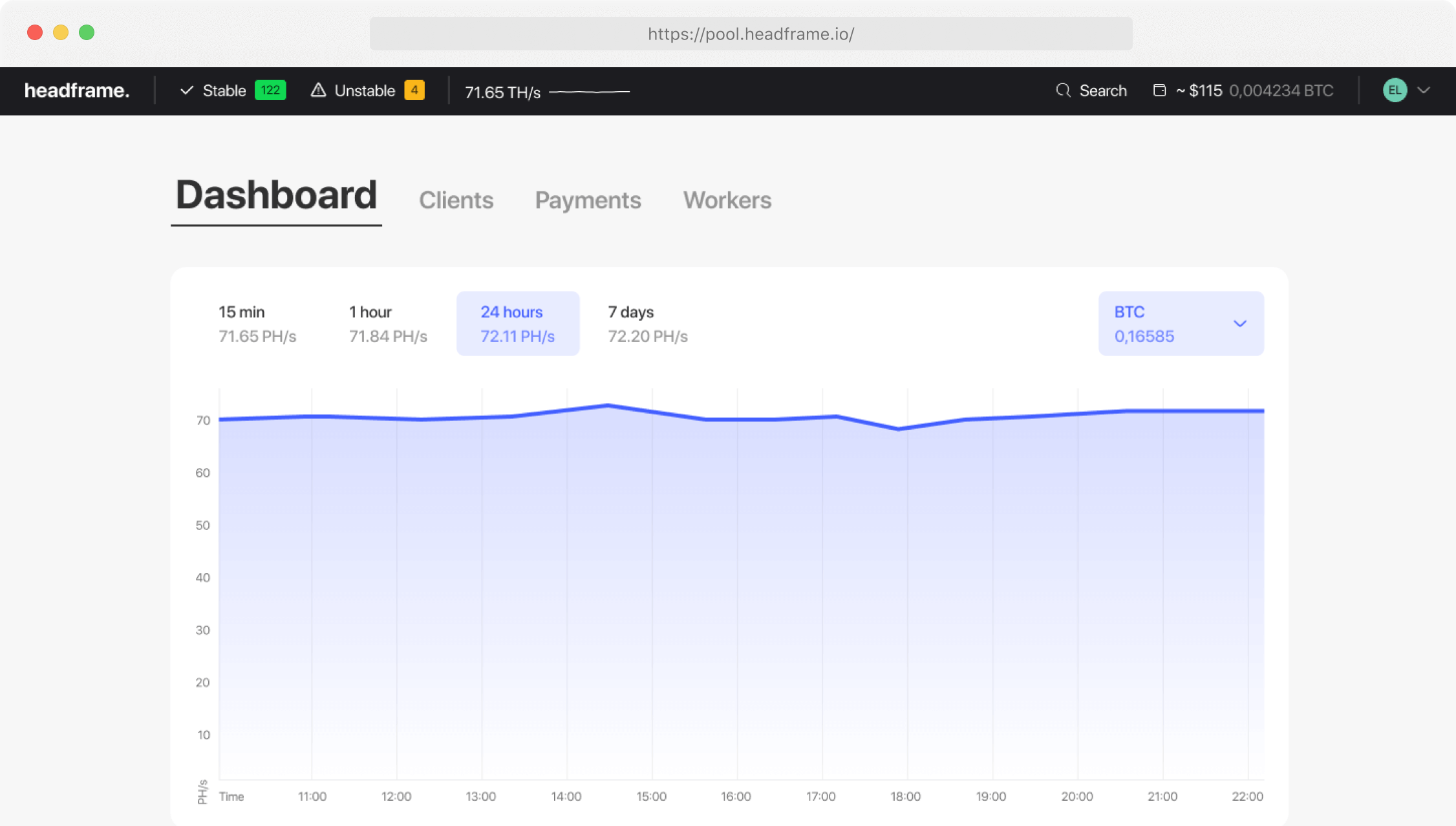
The essence of mining is finding a solution to a complex mathematical problem, which requires significant computing resources. In a mining pool, each participant contributes their share to the pool’s overall computing power, which significantly increases the chances of solving a block. When the pool successfully solves a block, the reward is distributed among the participants proportionally to the resources they contributed.
The process begins with a miner registering in the pool, after which they configure their mining equipment to work through the pool’s server. The pool servers coordinate the distribution of tasks among the participants and collect the results of their work. They also ensure the correctness of solutions and record successful attempts in the blockchain.
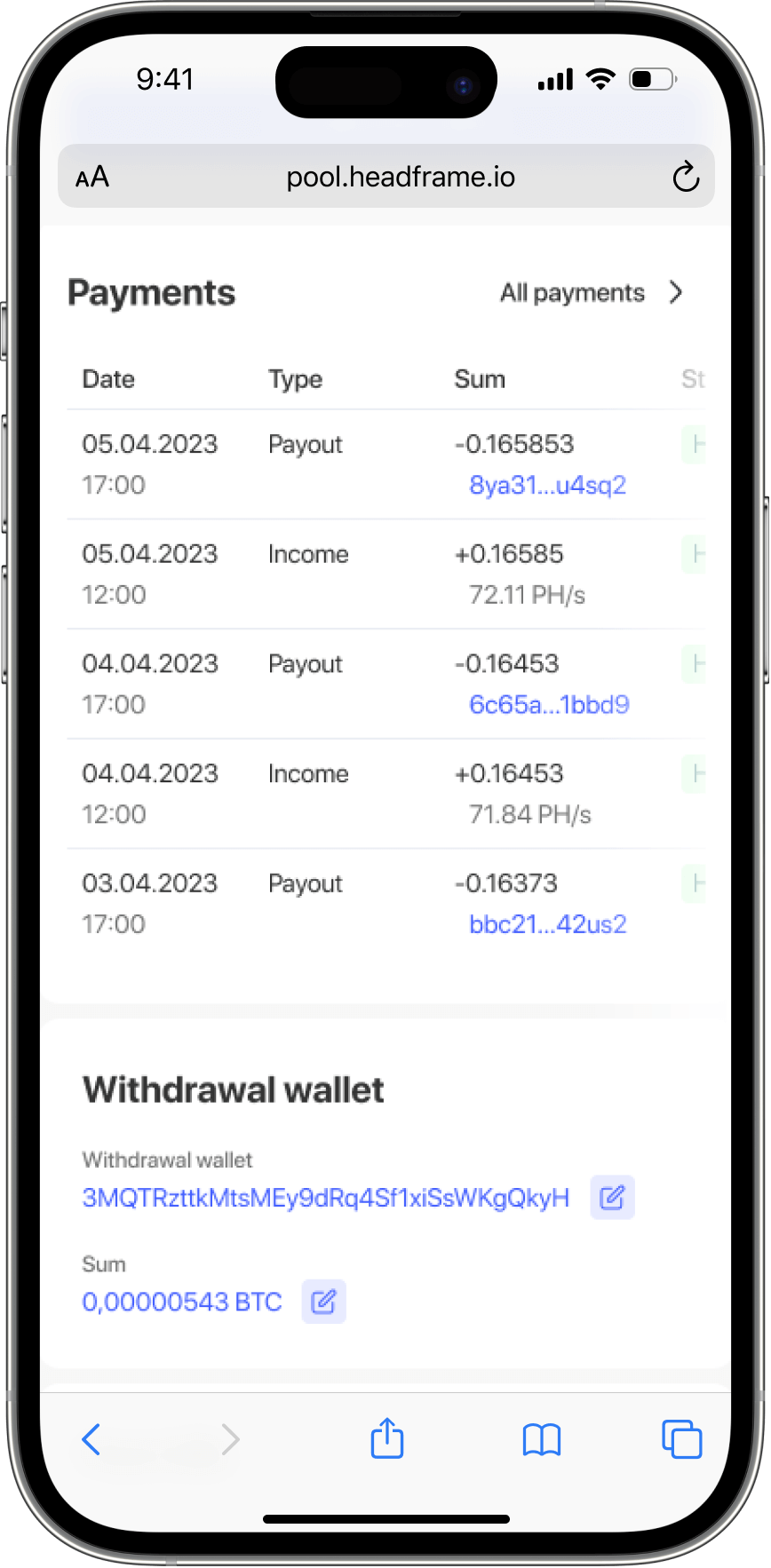
One of the key aspects of a mining pool’s operation is the reward distribution mechanism. Different pools may use different methods to calculate each participant’s share. For example, some pools use a share system, where each miner’s contributed work share is considered when distributing rewards. Others may use the Pay Per Last N Shares (PPLNS) system, which rewards miners for their contributions to the last solved blocks before finding the correct solution.
Pools also usually charge a fee for their services, which helps maintain their operational activities. These fees can vary, and miners should carefully assess how the pool’s fees may affect their potential profit.
From a security standpoint, mining pools are significant targets for cyberattacks since they handle large volumes of cryptocurrencies. Pools use various protection methods, including encryption of connections and authorization, to safeguard participants’ data and rewards. Resistance to attacks and protecting miners’ interests are critical aspects for maintaining trust and the pool’s stable operation.
Mining pools also play an important role in the decentralization of mining. Although there is a risk of power centralization in the hands of a few large pools, they also provide small miners the opportunity to participate in mining and earn profits, which would be significantly harder with solo mining.
Moreover, mining pools enhance mining efficiency through the optimization of task distribution and resource usage. This allows for the reduction of overall energy consumption in cryptocurrency mining, an important aspect given the increasing focus on the environmental impact of the cryptocurrency industry.
In conclusion, mining pools are a key element of the blockchain ecosystem, supporting the functioning and development of cryptocurrency networks. They not only help secure the blockchain by increasing the computing power needed to maintain its operation but also provide miners the opportunity to fairly share rewards for mining new blocks, making the process more accessible and profitable.