Social Impact of Mining Pools on Local Communities
Mining pools play a significant role in the development of the cryptocurrency industry by uniting the efforts of many miners for more efficient extraction of digital assets. However, their influence extends beyond the technological sphere, affecting the local communities where they are located. The social impact of mining pools on local communities includes economic, environmental, and social aspects that shape the living conditions of local residents and the state of the environment. Let’s explore how mining pools impact local communities and the consequences for their development.
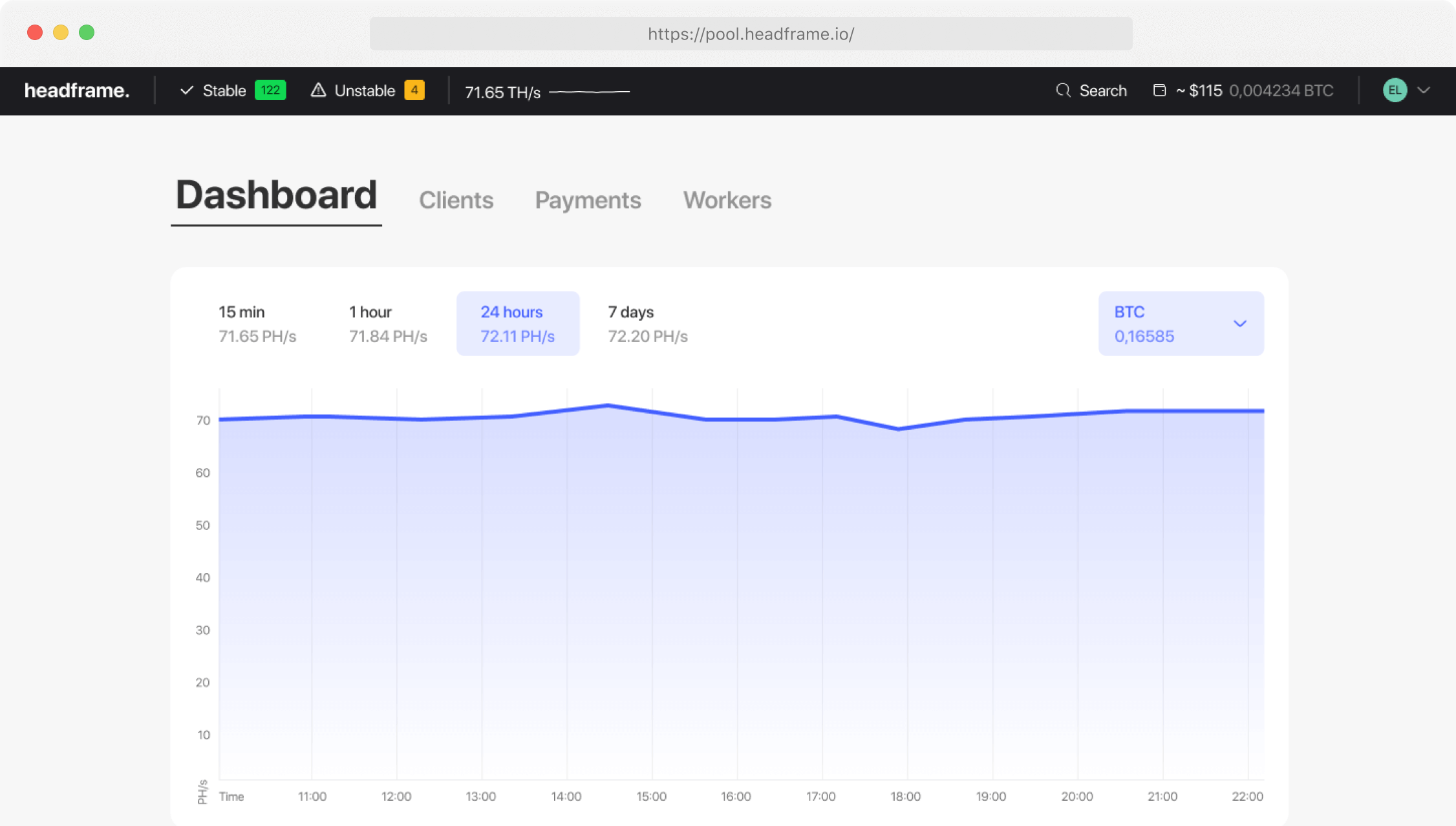
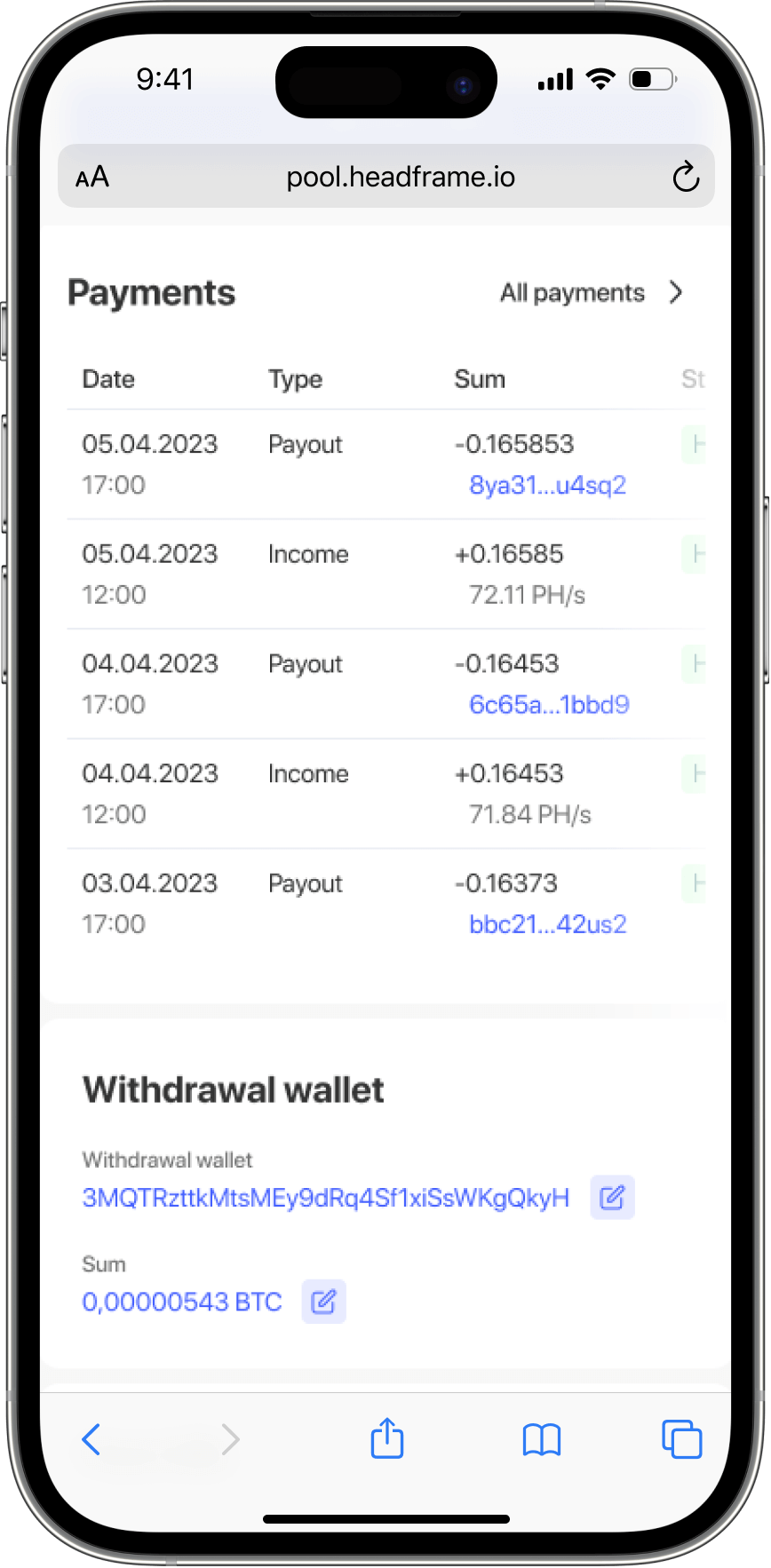
Earn more money with Headframe
Получите лучшую доходность в майнинге. Самая низкая на рынке комиссия 0.9%, обход блокировок и ежедневные бесплатные выплаты.
Economic Impact
The economic impact of mining pools on local communities often manifests through job creation and investment attraction. Mining requires significant computational power and energy, creating demand for qualified specialists in information technology, energy, and equipment maintenance. This contributes to job creation, positively affecting the local economy. Additionally, mining pools can attract investments in infrastructure development, such as building data centers and power plants, further promoting regional economic growth.
However, the economic impact of mining pools is not always straightforward. High demand for electricity can lead to increased energy prices, negatively affecting other industries and local residents. Moreover, automation and high technological requirements may limit access to jobs for unskilled workers, potentially causing social inequality. Therefore, it is essential to consider both the positive and negative economic consequences of mining activities.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of mining pools on local communities is also significant. Cryptocurrency mining requires large amounts of electricity, potentially increasing CO2 emissions and other pollutants, especially if energy is sourced from fossil fuels. This can negatively affect air quality and the health of local residents. Additionally, creating mining farms may require significant land resources, leading to landscape changes and ecological disruptions.
On the other hand, some mining pools actively work to reduce their environmental footprint by using renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower. This helps reduce the carbon footprint and improve the environmental sustainability of mining operations. Implementing energy-efficient technologies also helps reduce energy consumption and mitigate the negative impact on the environment. Supporting environmental initiatives and participating in projects to restore and protect natural resources can contribute to improving the environmental situation in the region.
Social Impact
The social impact of mining pools on local communities also manifests through interactions with residents and participation in social projects. Mining pools can support local communities by providing funding for social programs, education, healthcare, and cultural events. This helps improve the quality of life for local residents and strengthens ties between mining pools and communities. Supporting local economies and creating opportunities for small and medium-sized businesses also contribute to the social and economic growth of regions.
However, the social impact of mining pools can also be negative. High levels of noise and heat radiation from mining farms can cause inconvenience for local residents. Additionally, the rapid growth of mining pools and the increasing number of workers can lead to social tensions and competition for resources such as housing and services. It is important to consider these factors and take measures to minimize negative consequences to ensure harmonious development of mining pools and local communities.
Interaction with Local Authorities
Interaction between mining pools and local authorities and regulators also plays a crucial role in shaping their social impact. Compliance with legislative and regulatory requirements helps ensure the legitimacy and transparency of mining activities. Active cooperation with local authorities and participation in discussions and the development of regulatory norms contribute to creating a sustainable and predictable environment for mining operations. This strengthens the trust of local residents and investors in mining pools and supports their long-term development.
Educational Initiatives
Educational initiatives and upskilling local residents can also significantly enhance the social impact of mining pools. Training local residents in new mining methods and technologies helps them acquire the necessary skills and knowledge, contributing to job creation and improving the region’s economic situation. Educational programs and training sessions also help improve interactions between mining pools and local communities, promoting more responsible and informed participation in mining operations.
Partnerships and Collaboration
Partnerships and collaboration with local organizations and businesses also play an essential role in enhancing the social impact of mining pools. Combining efforts and sharing knowledge and resources help accelerate infrastructure and technology development and create new opportunities for local residents and businesses. Partnership relationships foster the creation of a global ecosystem where innovations can quickly spread and adapt to various conditions. This improves the overall efficiency and sustainability of mining operations and supports local communities.
In conclusion, the social impact of mining pools on local communities is a complex and multifaceted issue, encompassing economic, environmental, and social aspects. Job creation, investment attraction, community support, interaction with authorities, educational initiatives, and partnerships play crucial roles in shaping positive social impact. At the same time, it is important to consider and minimize negative consequences such as rising energy prices, environmental pollution, social inequality, and inconvenience for local residents. Understanding and applying these strategies help mining pools effectively interact with local communities and achieve sustainable development in the cryptocurrency industry.