Impact of Political Events on Mining Pool Stability
Political events play a significant role in shaping the stability of mining pools. A mining pool is a collective of miners that enhances the chances of successfully mining cryptocurrency and distributing rewards. However, political instability, legislative changes, and other political factors can significantly impact the operation of these collectives. This article will examine how political events can affect the stability of mining pools and what measures can be taken to minimize these risks.
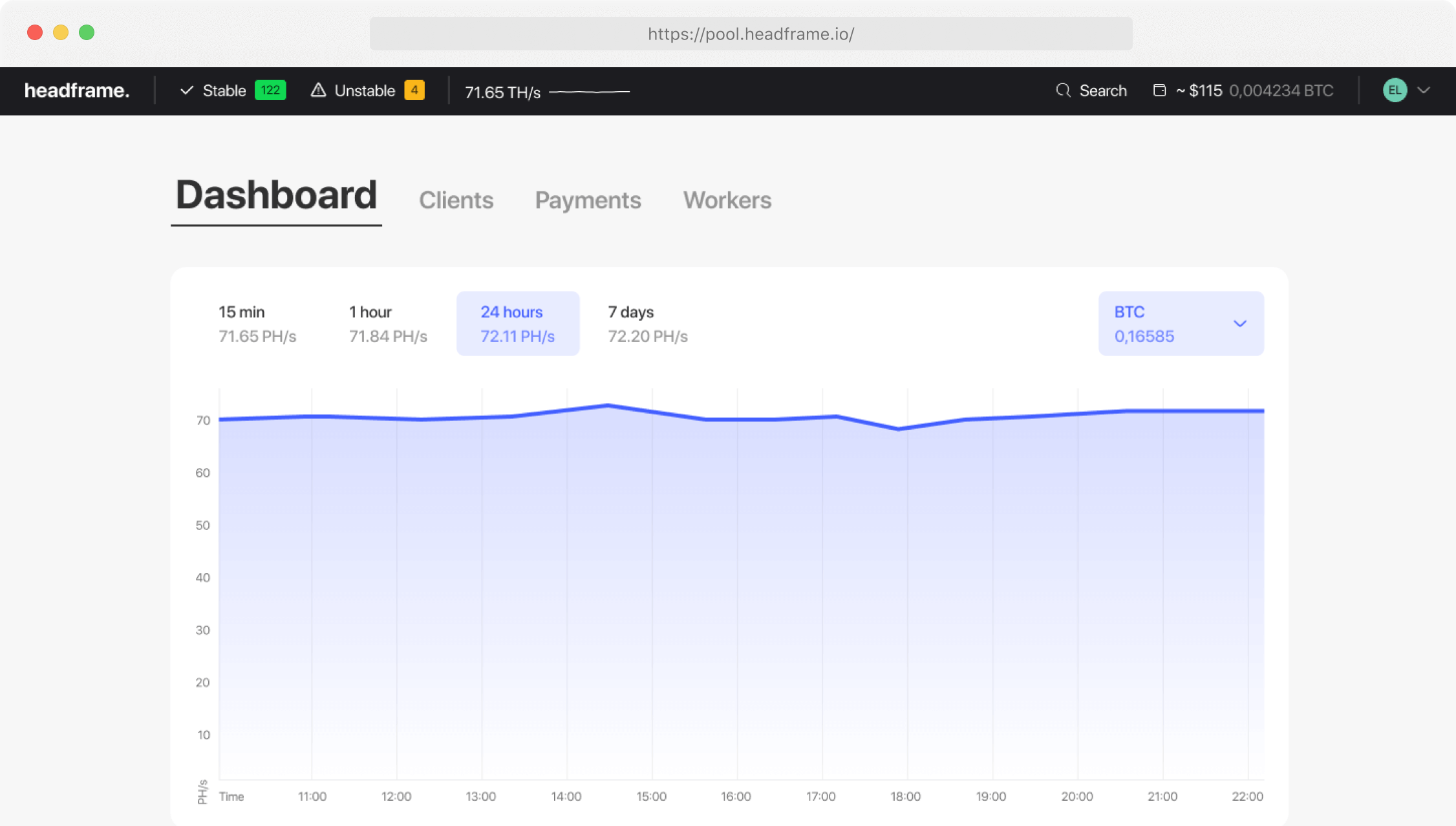
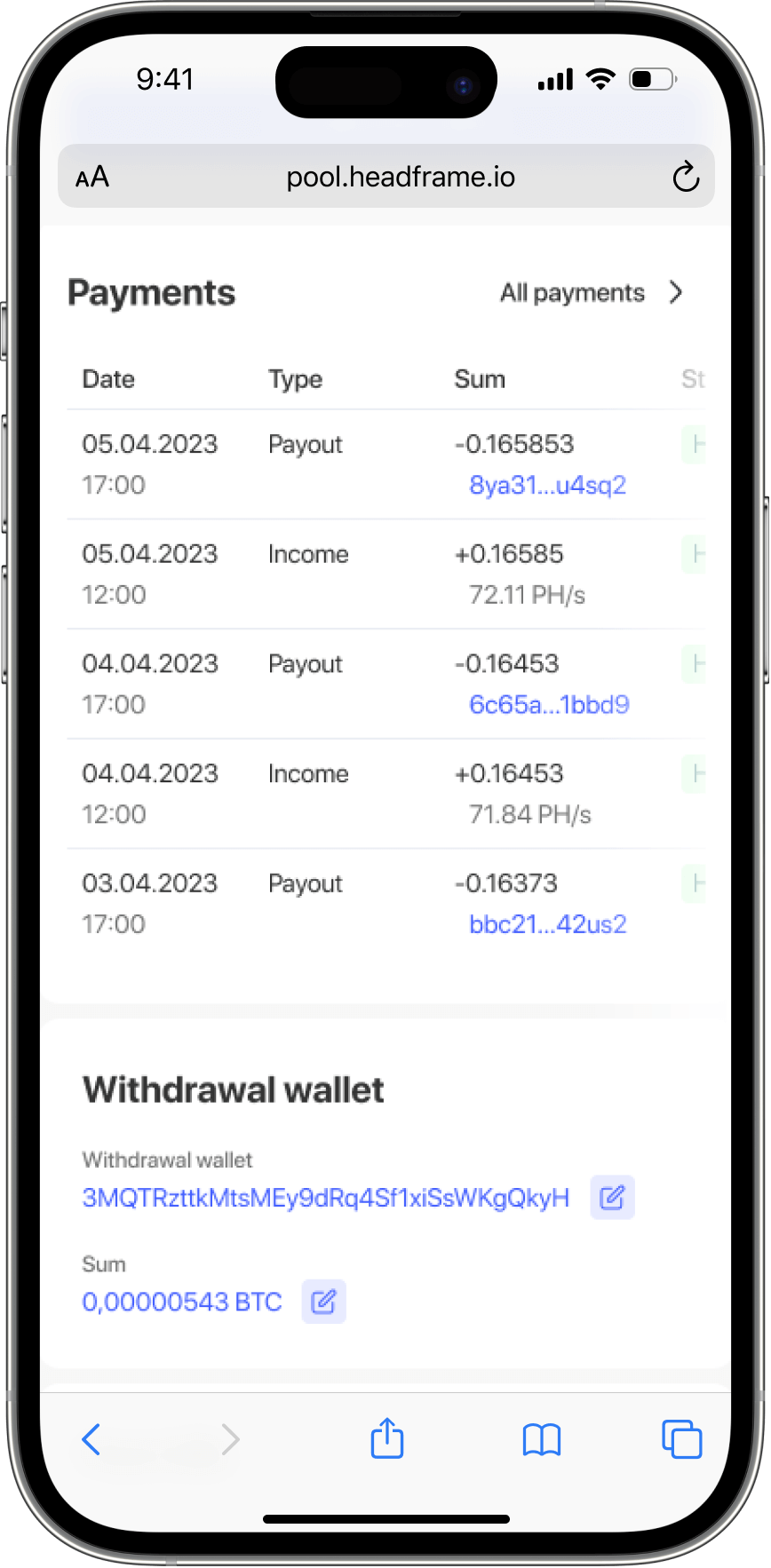
Earn more money with Headframe
Получите лучшую доходность в майнинге. Самая низкая на рынке комиссия 0.9%, обход блокировок и ежедневные бесплатные выплаты.
Political instability, including changes in government, conflicts, and social unrest, can create significant obstacles for the operation of mining pools. For instance, political instability in a particular country can lead to disruptions in electricity supply, negatively affecting the productivity of mining pools. Electricity is a key resource for mining, and its availability directly impacts the ability of pools to maintain consistent and predictable operations.
Changes in legislation also have a substantial impact on mining pools. Governments can introduce new laws and regulations directly affecting the cryptocurrency sector. For example, the ban on cryptocurrency mining imposed in China in 2021 forced many mining pools to cease operations or relocate to other countries. Such abrupt changes in the legal environment create significant risks for the stability of mining pools, forcing them to adapt to new conditions or seek more stable jurisdictions.
Additionally, the introduction of new taxes and fees on cryptocurrency-related activities can increase the operational costs of mining pools. Higher tax burdens can make mining less profitable, potentially leading to a decrease in the number of pool participants and a reduction in their overall power. Under increased tax pressure, mining pools must find ways to optimize their costs and increase efficiency to remain competitive.
Political decisions in the energy sector also significantly affect the stability of mining pools. Government policies aimed at limiting the use of hydrocarbon energy sources and promoting renewable energy can influence the availability and cost of electricity for miners. In countries where traditional energy sources prevail, mining pools may face rising costs due to environmental regulations and emission reduction requirements. In such conditions, transitioning to renewable energy sources can become a strategic decision to maintain stability and reduce operational expenses.
The state’s economic policy, including capital control measures and currency restrictions, also impacts mining pools. For instance, in countries with strict currency control, miners may find it difficult to convert earned cryptocurrency into fiat money, creating additional financial risks. Economic instability, high inflation, and currency crises can complicate financial operations and reduce the attractiveness of mining in such countries.
The influence of international politics on mining pools should also not be underestimated. Sanctions and trade restrictions can limit miners’ access to necessary equipment and technologies. For example, trade sanctions against certain countries can lead to a shortage of mining equipment and an increase in its cost. This complicates the modernization and expansion of pools, reducing their competitiveness on a global level.
The reaction of mining pools to political events often includes risk diversification. One way to minimize political risks is geographic diversification of capacities. Distributing mining farms across different countries and regions reduces dependence on the political and economic stability of a single jurisdiction. This also helps mining pools remain flexible and quickly adapt to changes in the international political landscape.
Close cooperation with local authorities and participation in dialogue with regulators also help mining pools adapt to political changes. Establishing good relationships with local governments can provide a more predictable and stable operational environment. Mining pools can participate in shaping legislation by providing expert consultations and arguments for reasonable regulation that considers the interests of all market participants.
Strategic planning and preparation for possible political changes also play a key role in maintaining the stability of mining pools. Analyzing political risks, developing event scenarios, and creating contingency plans help pools respond promptly to changes and minimize potential losses. This includes monitoring the political situation, forecasting possible legislative changes, and developing strategies for rapid relocation or adaptation of operations.
Technological development and innovations in mining can also contribute to the resilience of mining pools in the face of political instability. Adopting new technologies, such as more energy-efficient mining installations and distributed mining methods, can reduce dependence on traditional resources and mitigate the impact of political factors. Mining pools investing in advanced technologies and continually improving their operational processes have better chances of long-term success.
In conclusion, political events significantly impact the stability of mining pools, affecting various aspects of their activities. From legislative changes and energy policies to international sanctions and economic instability, all these factors can pose serious challenges for mining pools. However, through strategic diversification, close cooperation with regulators, technological innovations, and careful planning, mining pools can successfully adapt to changes and maintain their stability in a constantly changing political environment.