Interaction of Mining Pools with Traditional Financial Institutions
Mining pools, as critical participants in the cryptocurrency industry, are beginning to play a significant role in modern financial systems. Their interaction with traditional financial institutions opens up new opportunities and challenges for both sides, especially in the context of the gradual recognition and integration of cryptocurrencies into mainstream finance.
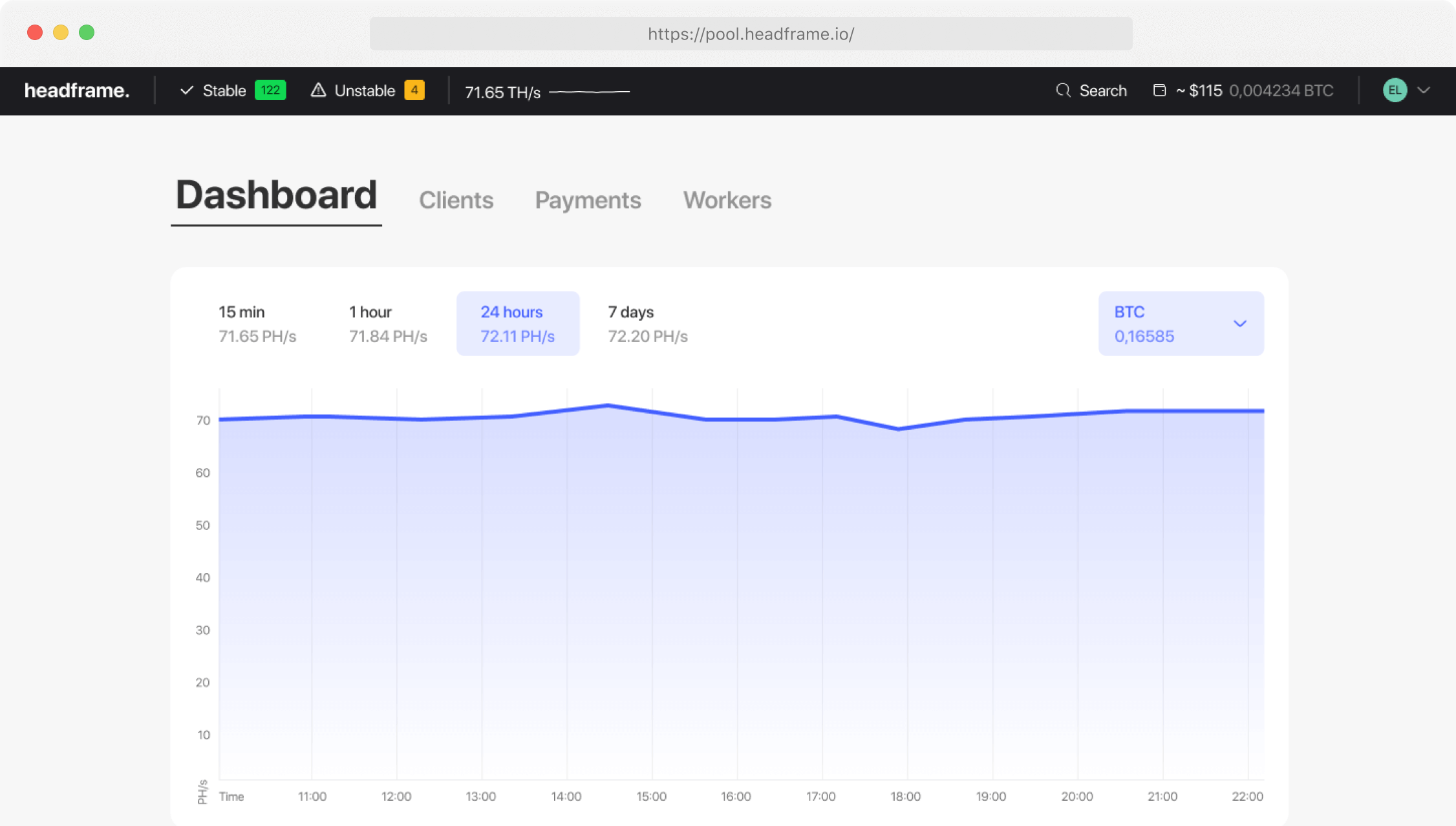
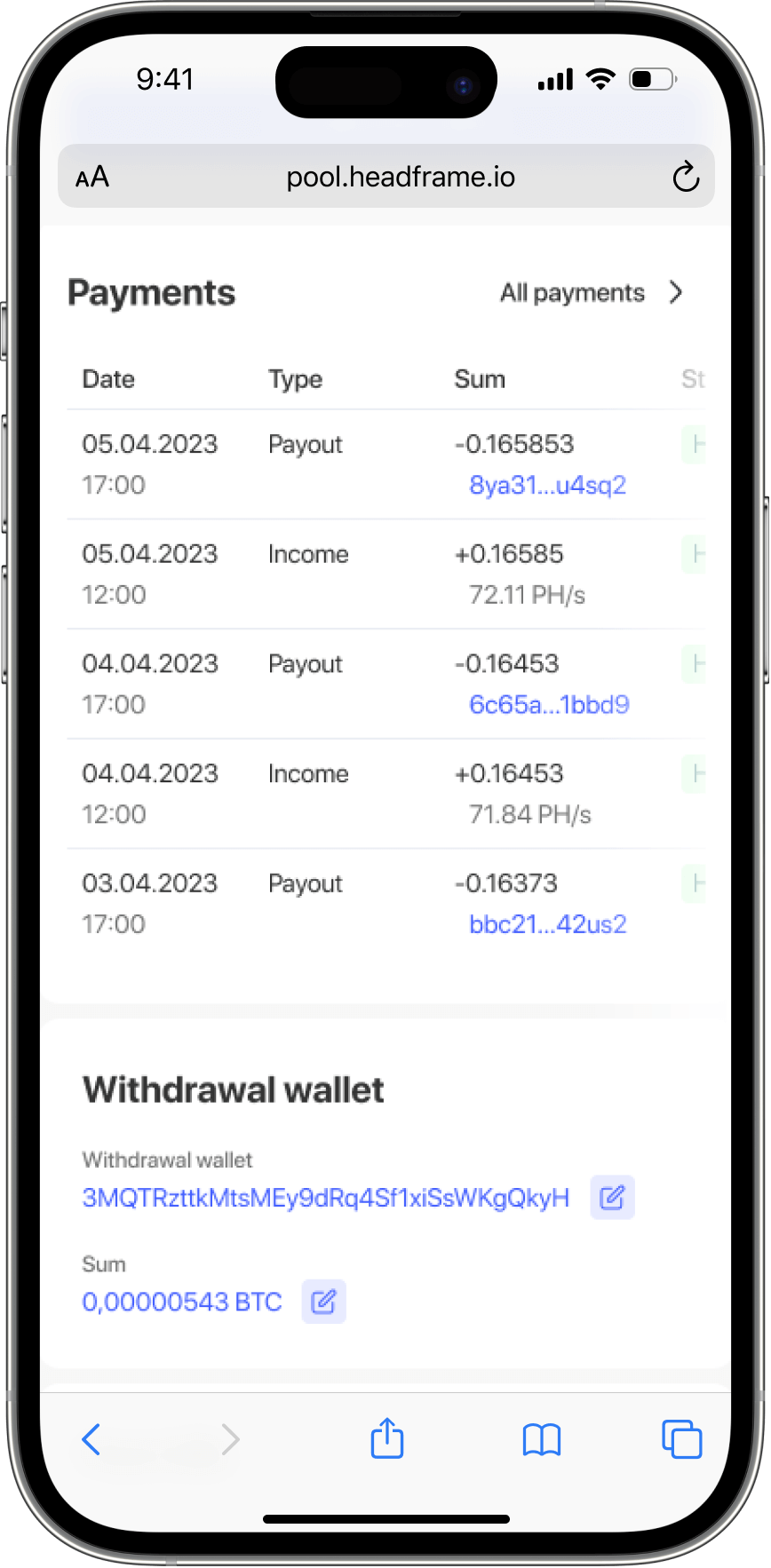
Earn more money with Headframe
Join a mining pool and get the best profitability in mining. Already more than 10,000 miners trust Headframe.
Traditional financial institutions have historically viewed cryptocurrencies with caution, perceiving them as high-risk assets due to their volatility, anonymity, and regulatory risks. However, with increasing institutional interest in cryptocurrencies, banks and other financial organizations have started exploring ways to collaborate with mining pools, which play a key role in ensuring the stability and security of cryptocurrency networks.
One of the main forms of interaction has been the financing of mining pool operations. Financial institutions provide loans and investments in mining infrastructure, which requires significant capital investment, especially in acquiring specialized equipment and creating data centers. This collaboration allows mining pools to scale their operations, ensuring higher productivity and stability.
On the other hand, financial institutions find partners in mining pools to develop their cryptocurrency market products, including custodial services (cryptocurrency storage), asset management, and brokerage services. Collaboration with mining pools allows banks and financial firms to gain expertise in blockchain technologies and cryptocurrencies, which is a crucial aspect in a rapidly evolving market.
Regulatory issues remain a significant barrier in the relationship between mining pools and traditional financial institutions. Taxation and anti-money laundering legislation pose challenges in creating transparent and legally clear interaction schemes. While some countries have developed clear regulatory frameworks, others are still in the process of discussing and adopting legislation, creating uncertainty for both sides. Mining pools and financial institutions must closely monitor legislative changes to adapt to new requirements in a timely manner and minimize risks.
Additionally, there is a problem of reputational risks for financial institutions associated with cryptocurrency volatility and potential security risks related to blockchain technologies. However, with the constant improvement of technologies and the increasing number of successful use cases of cryptocurrencies, these risks are gradually decreasing. Financial institutions that can overcome initial difficulties and effectively integrate into the digital economy can significantly benefit from timely entry into this field.
The interaction of mining pools with traditional financial institutions also opens new opportunities for innovation in financial technologies. This collaboration can stimulate the development of new financial products, such as cryptocurrency derivatives or integrated payment solutions, which can provide greater flexibility, security, and accessibility of financial services to a wide range of users.
In conclusion, the interaction between mining pools and traditional financial institutions represents a complex but promising process that requires both sides to be ready for innovation, accept challenges, and adapt to the rapidly changing landscape of financial and technological markets. Collaboration in this area not only fosters the development of the cryptocurrency sector but also enriches traditional financial systems with new tools and opportunities, making them more resilient and relevant to modern economic conditions.