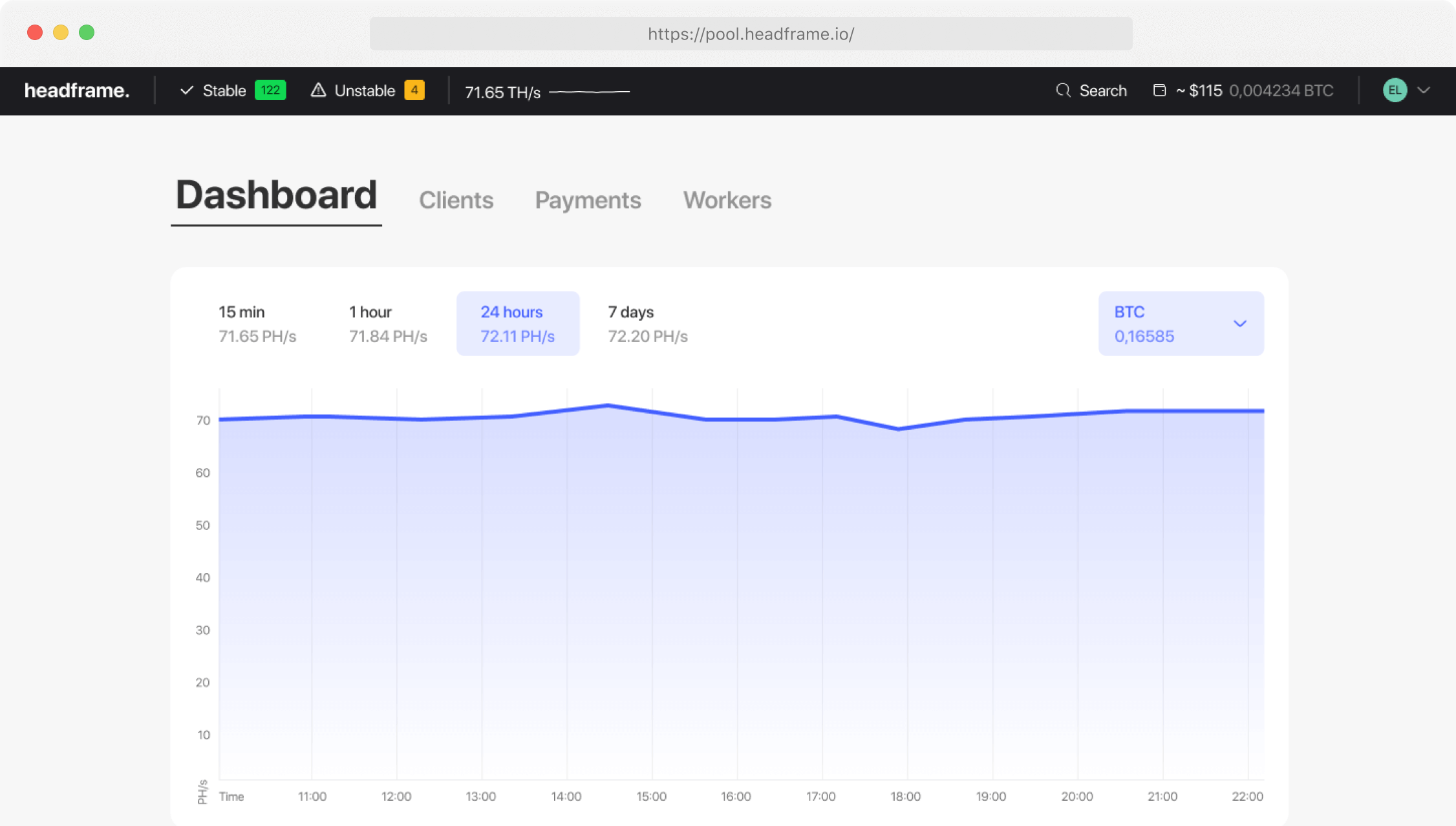
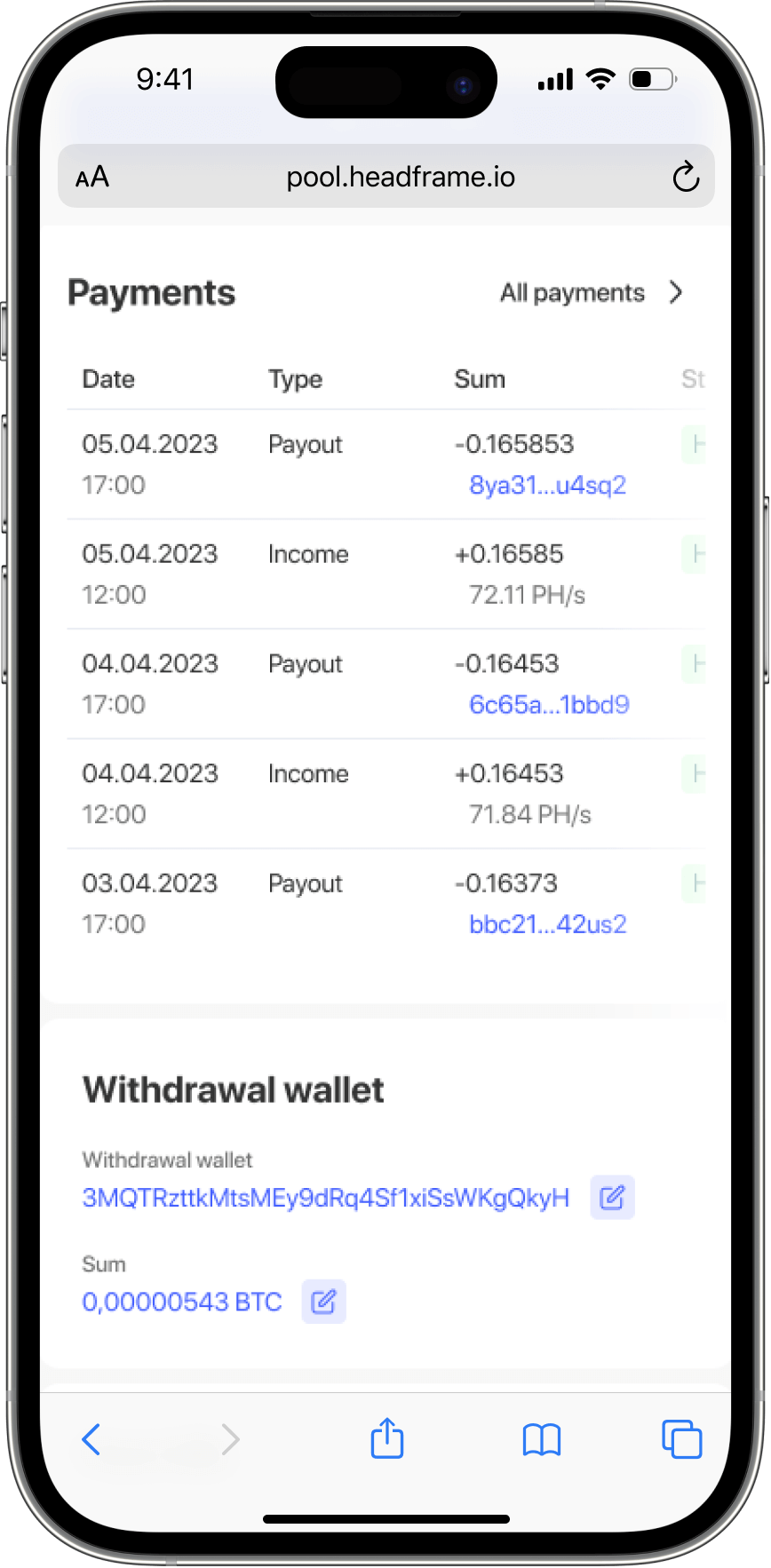
The evolution of mining pools: From genesis to today
The world of cryptocurrency mining has seen dramatic changes since the inception of Bitcoin in 2009. One of the most significant developments in this space is the advent of mining pools. These collaborative groups have transformed the landscape of cryptocurrency mining, making it more accessible and efficient for miners worldwide. Understanding the evolution of mining pools from their inception to the present day provides valuable insights into their impact on the cryptocurrency ecosystem and the key milestones that have shaped their development.
Earn more money with Headframe
Join a mining pool and get the best profitability in mining. Already more than 10,000 miners trust Headframe.
Mining pools were born out of necessity as the difficulty of mining Bitcoin increased. In the early days of Bitcoin, solo mining was the norm. Individual miners used their personal computers to solve cryptographic puzzles and validate transactions, earning rewards in the form of new bitcoins. The process was relatively straightforward and profitable, as the network difficulty was low, and the competition was minimal.
However, as more miners joined the network and the popularity of Bitcoin grew, the mining difficulty increased exponentially. This rise in difficulty made it harder for individual miners to solve puzzles and earn rewards. The need for greater computational power and more efficient mining methods became apparent. Enter mining pools, a revolutionary concept that allowed miners to combine their resources and share the rewards, thus increasing their chances of success.
The first mining pool, Slush Pool, was established in 2010 by Marek Palatinus, also known as Slush. This pioneering pool introduced the concept of pooling resources to mine Bitcoin more effectively. By joining Slush Pool, miners could collectively work on solving cryptographic puzzles, and when a block was successfully mined, the rewards were distributed among the participants based on their contributed computational power. This collaborative approach marked a significant shift in the mining landscape, making it more feasible for individual miners to participate and earn rewards.
Following the success of Slush Pool, several other mining pools emerged, each bringing innovations and improvements to the model. These pools varied in terms of fee structures, payout methods, and supported cryptocurrencies, catering to the diverse needs of miners. The introduction of pay-per-share (PPS) and pay-per-last-n-shares (PPLNS) payout methods provided miners with options to choose the payment structure that best suited their risk tolerance and mining capacity.
As mining pools grew in popularity, so did the development of specialized mining hardware. The transition from CPU mining to GPU mining and eventually to ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) mining drastically increased the computational power available to miners. This hardware evolution further fueled the growth of mining pools, as the increased difficulty of mining made solo mining less viable for most individuals. Pools allowed miners to leverage their hardware investments more effectively, ensuring a steadier stream of rewards.
The rise of mining pools also brought about greater centralization in the mining process, a development that sparked debates within the cryptocurrency community. While pools made mining more accessible and efficient, they also concentrated mining power in the hands of a few large pools. This centralization posed potential risks to the network’s security and decentralization, as a single pool controlling more than 50% of the network’s hash rate could theoretically execute a 51% attack, manipulating transactions and undermining trust in the blockchain.
Despite these concerns, mining pools continued to evolve and innovate. The development of multi-pool mining allowed miners to switch between different cryptocurrencies based on profitability, maximizing their earnings. This flexibility became increasingly important as the cryptocurrency market diversified and new digital assets emerged. Multi-pool mining software enabled miners to dynamically allocate their computational resources, ensuring optimal performance across various blockchain networks.
Another significant milestone in the evolution of mining pools was the introduction of decentralized mining pools. Unlike traditional pools, which rely on a central server to coordinate mining efforts, decentralized pools distribute the mining process across a network of nodes. This approach enhances the security and resilience of the mining pool by eliminating single points of failure and reducing the risk of centralized control. Decentralized mining pools align more closely with the core principles of blockchain technology, promoting greater decentralization and security.
The evolution of mining pools also saw the integration of advanced security measures to protect miners’ contributions and earnings. Features such as two-factor authentication, encryption, and DDoS protection became standard offerings, providing miners with enhanced security and peace of mind. Regular security audits and transparency in operations further bolstered trust in mining pools, ensuring that miners could rely on fair and ethical practices.
As the cryptocurrency mining industry matured, regulatory developments also began to influence the operation of mining pools. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide started to recognize the significance of cryptocurrency mining and introduced guidelines to ensure compliance with financial and environmental standards. Mining pools adapted to these regulatory changes by implementing measures to enhance transparency and accountability, such as KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) procedures.
The environmental impact of cryptocurrency mining emerged as a critical issue, prompting mining pools to explore sustainable practices. The high energy consumption associated with mining led to concerns about its carbon footprint. In response, some mining pools began to invest in renewable energy sources and optimize their operations for greater energy efficiency. These efforts aimed to reduce the environmental impact of mining and promote sustainable practices within the industry.
The current landscape of mining pools is characterized by a diverse array of options catering to different types of miners, from individual hobbyists to large-scale operations. The continuous evolution of mining technology, coupled with the adaptability of mining pools, ensures that they remain a vital component of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. As blockchain technology advances and new consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-stake (PoS), gain traction, mining pools will continue to evolve to meet the changing needs of miners and the broader market.
Looking ahead, the future of mining pools will likely be shaped by ongoing technological advancements, regulatory developments, and market dynamics. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in mining operations holds the potential to further optimize performance and efficiency. Additionally, the development of more sustainable and eco-friendly mining practices will play a crucial role in addressing environmental concerns and ensuring the long-term viability of cryptocurrency mining.
In conclusion, the evolution of mining pools from their inception to the present day highlights their critical role in the cryptocurrency mining landscape. From the early days of Slush Pool to the advanced, secure, and decentralized pools of today, mining pools have continually adapted to meet the needs of miners and the broader market. Understanding this evolution provides valuable insights into the impact of mining pools on the cryptocurrency ecosystem and the key developments that have shaped their growth. As the industry continues to evolve, mining pools will remain a cornerstone of cryptocurrency mining, driving innovation and ensuring the efficient operation of blockchain networks.