How Changes in Mining Difficulty Affect Pool Profitability
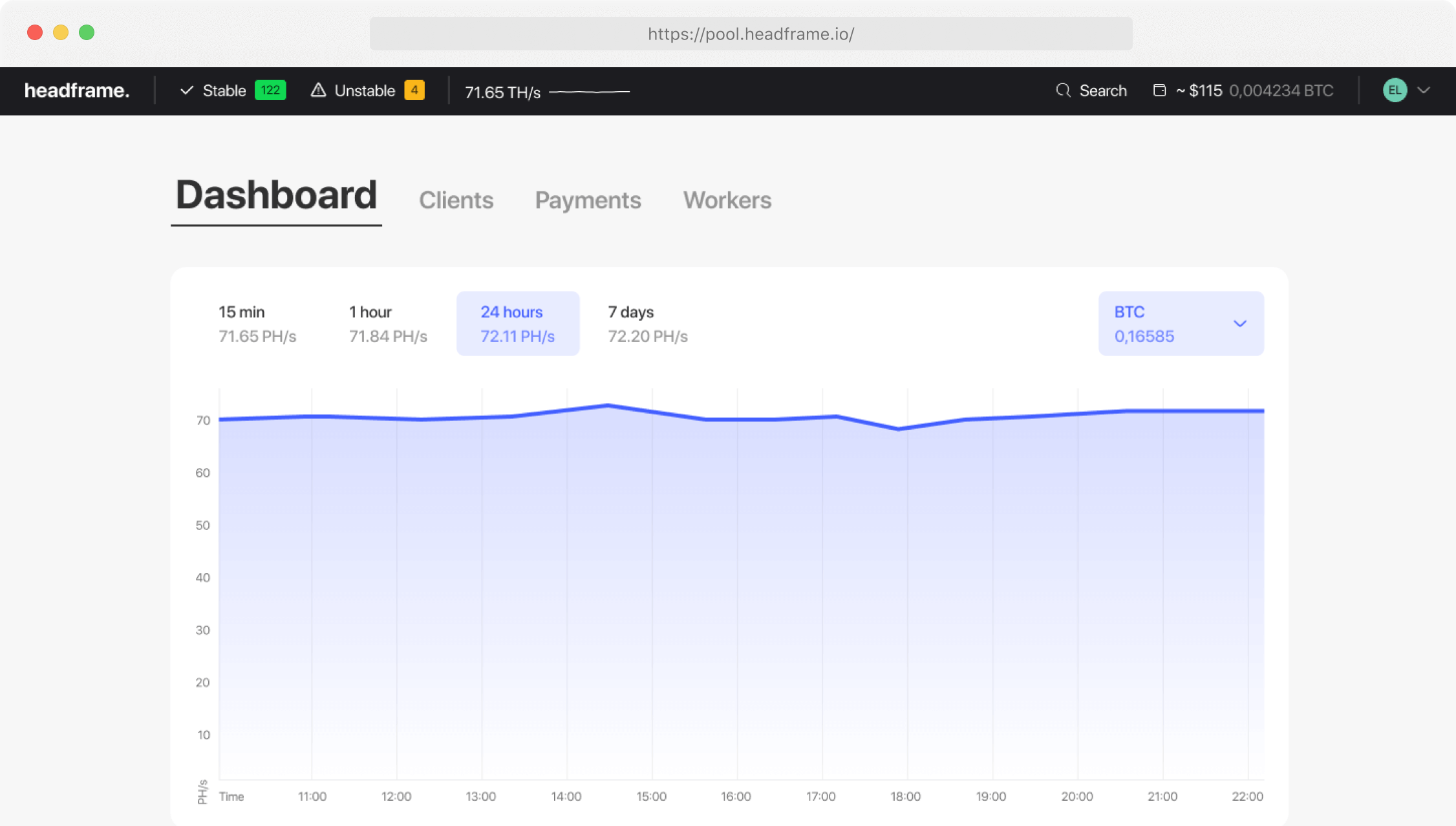
In the world of cryptocurrencies, mining difficulty is a dynamic factor that directly affects the profitability of mining for both individual miners and mining pools. Mining difficulty is automatically adjusted by the cryptocurrency network based on the total computing power dedicated to mining. This is done to ensure that the average time to find a new block remains constant. Such adjustments have significant implications for all participants in the process.
Earn more money with Headframe
Join a mining pool and get the best profitability in mining. Already more than 10,000 miners trust Headframe.
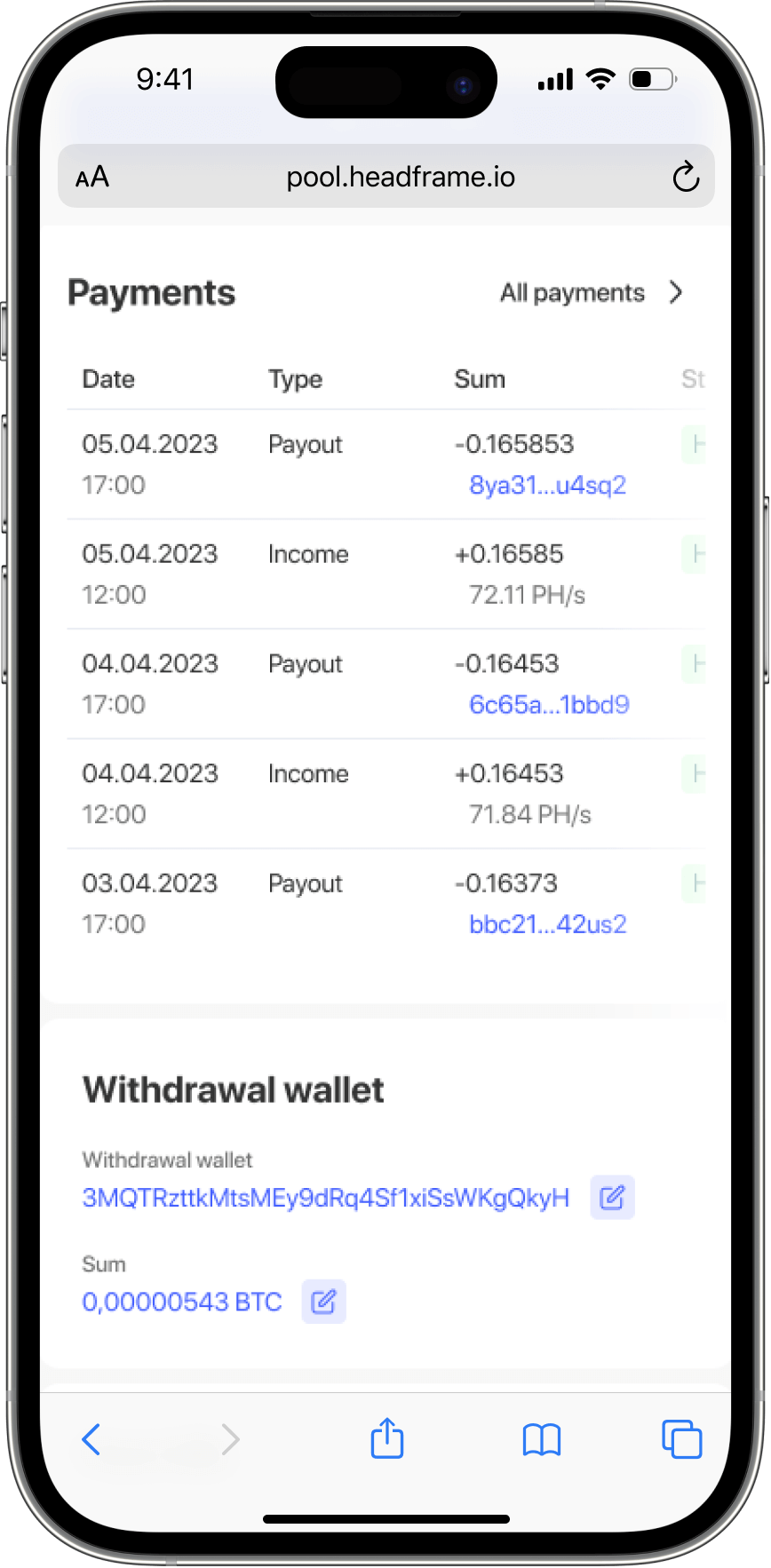
When mining difficulty increases, it means that more time and computational power are required to find new blocks. As a result, each individual miner and mining pool receive fewer rewards for their efforts because the competition for each block intensifies. This leads to decreased mining profitability as electricity and other operational costs remain constant or even increase.
However, the increase in mining difficulty can also indicate growing interest in the cryptocurrency and an increase in the number of miners in the network, which, in turn, can lead to an increase in the cryptocurrency’s value. In such a case, even if the number of rewards per block decreases, the total value of these rewards in fiat currency can remain attractive or even increase.
Mining pools, recognizing these dynamic changes, often implement strategies to optimize their operations. They may invest in more powerful and efficient equipment, improve cooling methods to reduce energy costs, or choose more advantageous geographic locations for their servers. Additionally, many mining pools strive to offer their participants more favorable conditions, such as lower fees or additional services, to remain competitive in the market.
It is also important to note that mining difficulty can vary not only based on the number of miners but also due to technological advancements in mining equipment. For example, the development of new, more efficient types of mining ASIC chips can radically change the mining landscape, making more powerful equipment available that can handle increased difficulty more effectively. This, in turn, can temporarily increase the income of pools that are the first to adopt these technologies until the rest of the network adapts to the new conditions.
Socio-economic factors also play a role. Changes in cryptocurrency-related legislation can affect the cost of mining operations in various countries, which also influences the choice of server locations by mining pools. Political stability, electricity costs, and the availability of technological infrastructure are all significant factors determining where and how mining pools choose to locate their operations.
In the context of managing a mining pool, it is important not only to respond to current changes in mining difficulty but also to anticipate possible future trends. This requires in-depth market analysis, understanding of technological trends, and adaptation to rapidly changing conditions. For example, pools may invest in research and development of their own mining software to optimize its efficiency and reduce dependence on external developers.
Moreover, effective mining pools often strive to create a sustainable community around their platform by providing educational resources and support for miners. This not only helps retain current participants but also attracts new ones, which is important for maintaining and growing the overall computing power of the pool.
In conclusion, mining difficulty is a critical factor that affects all aspects of cryptocurrency mining. Mining pools that can flexibly adapt to changes in difficulty and anticipate future trends in technology and the market have the best chances of success. Managing a mining pool requires not only technical knowledge but also strategic planning to ensure its sustainability and profitability in the long term.