Mining Pools for Different Cryptocurrencies: Features and Approaches
Mining pools are collective groups that combine the resources of individual miners to increase their chances of successfully mining cryptocurrencies. Depending on the type of cryptocurrency the pool works with, the approaches to mining, technologies used, and reward distribution methods can vary significantly.
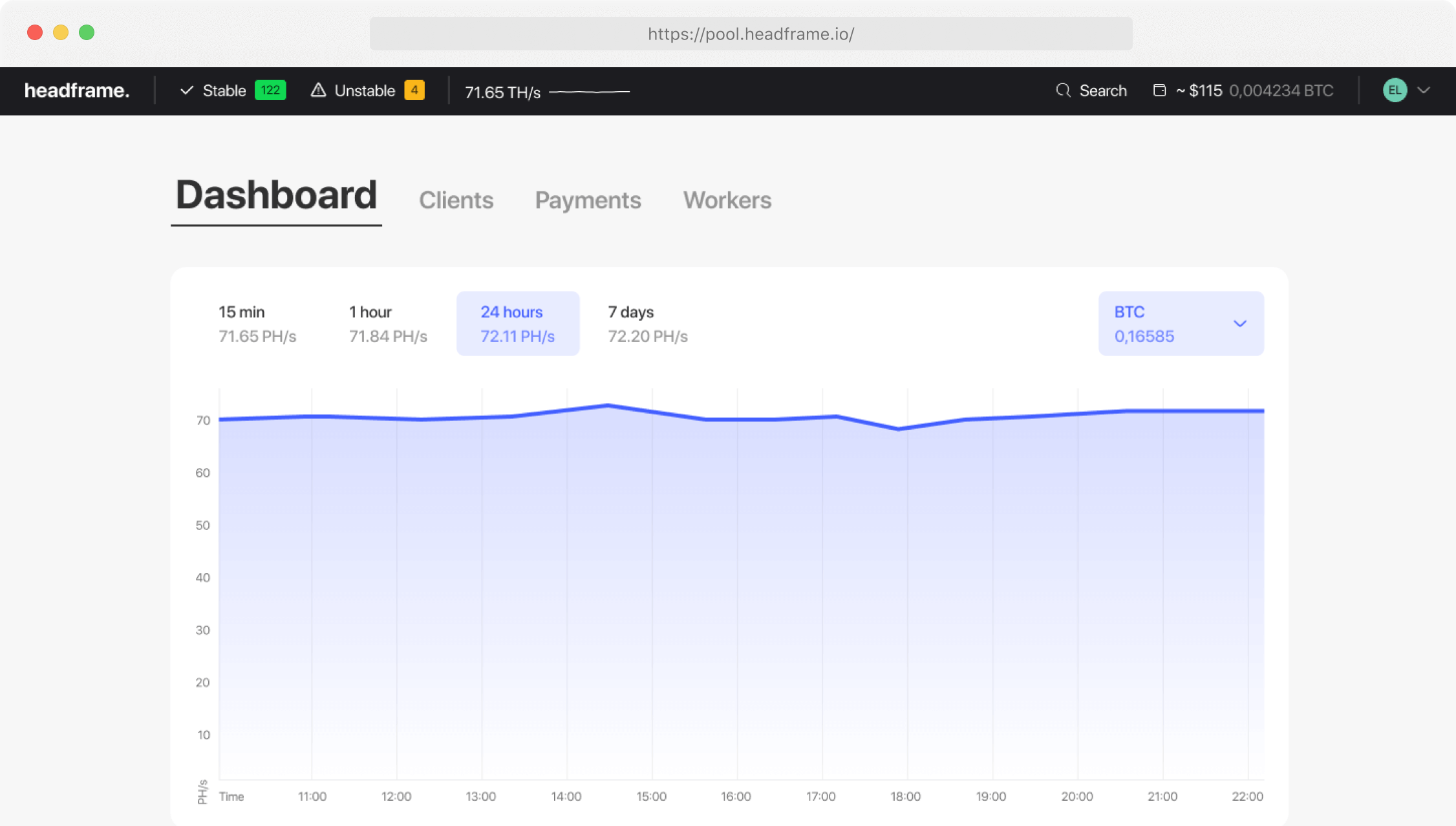
Earn more money with Headframe
Join a mining pool and get the best profitability in mining. Already more than 10,000 miners trust Headframe.
Each type of cryptocurrency has its technical features that determine the approaches to mining. For example, Bitcoin mining is based on the SHA-256 algorithm, which requires significant computing power and specialized equipment known as ASIC miners. This equipment is designed specifically to solve cryptographic tasks, making Bitcoin mining highly competitive. Therefore, Bitcoin mining pools are often structured to optimize the use of ASIC miners, minimize energy costs, and maximize output power.
For cryptocurrencies using algorithms like Scrypt, such as Litecoin, the equipment requirements and mining approaches differ. Scrypt was designed to be more accessible to users with regular computer equipment, making it less dependent on specialized hardware. Mining pools for such cryptocurrencies often have lower entry thresholds and offer opportunities for miners with limited resources.
Ethereum mining, which is transitioning from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS), presents a unique set of challenges. Mining pools working with Ethereum must be adapted not only to the current PoW requirements but also be prepared for the transition to PoS. This requires flexibility in resource management and strategy, as well as investments in software and hardware upgrades.
Security is a common concern for all types of mining pools, but the ways to ensure it may vary depending on the algorithm and the cryptocurrency used. Pools must protect their operations from external attacks such as double-spending or 51% attacks, especially in networks with lower overall computing power. Pools for smaller or less secure cryptocurrencies may require stricter security measures and more active risk management to ensure the reliability of their operations and protect participants’ funds.
The importance of reliable technical support and stable infrastructure cannot be underestimated, especially in mining pools dealing with volatile or less popular cryptocurrencies. Technical failures, transaction processing delays, or downtime can significantly reduce miners’ profitability and undermine trust in the pool. Pools must invest in high-quality servers, reliable software, and competent support teams to provide the best possible service to their participants.
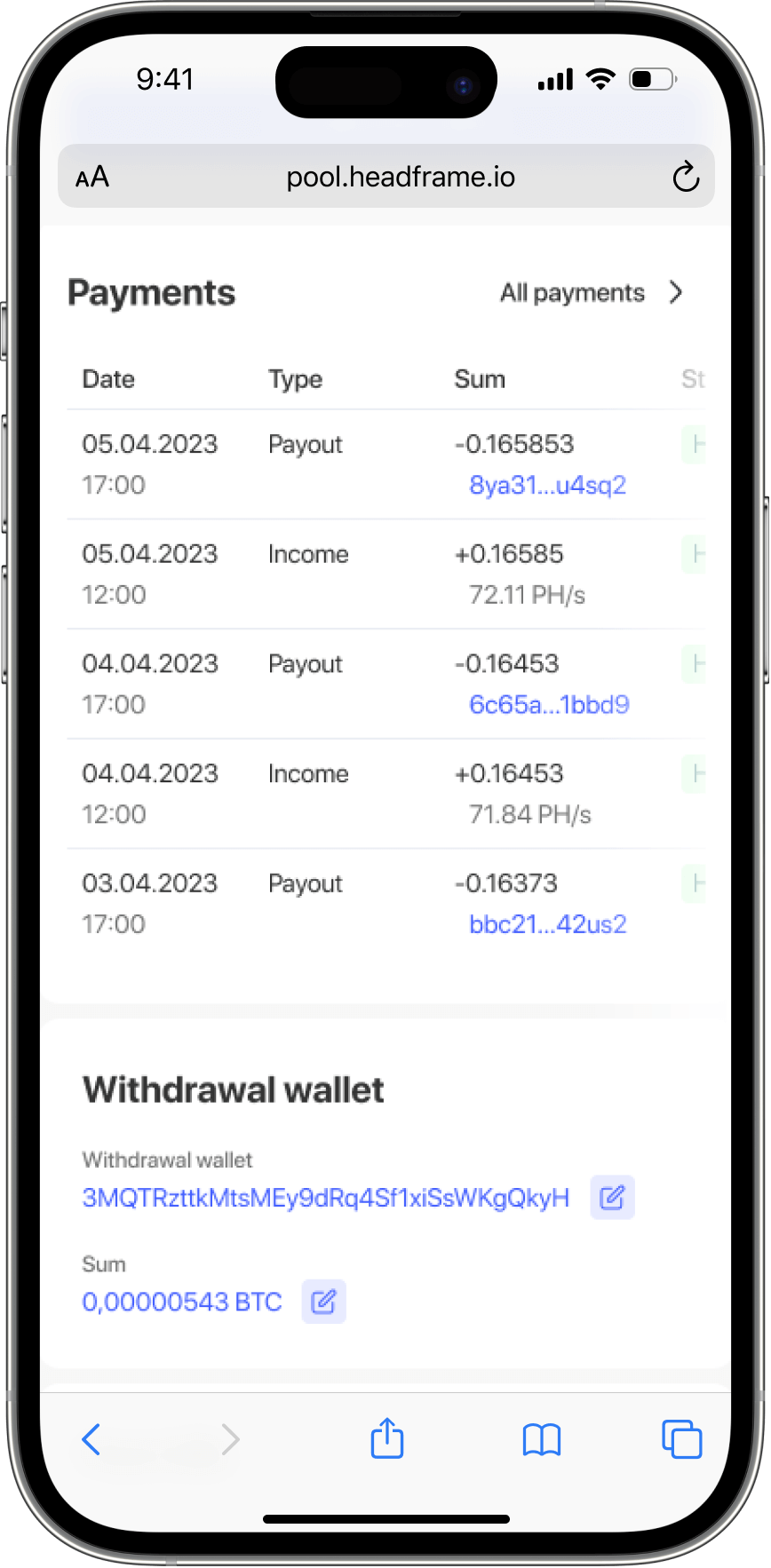
Commission structures also play a critical role in choosing a mining pool and can vary significantly depending on the type of cryptocurrency. Miners need to carefully study the conditions of each pool, paying attention to commission rates, payout calculation methods, and minimum payout thresholds. Pools offering lower commissions and more transparent conditions often attract more participants, but this must be combined with a good reputation and stable payouts.
Cultural and geographical aspects can also influence the choice and operation of mining pools. For example, pools located in certain countries or regions may provide services better adapted to local legislative and tax requirements. It may also be more convenient to work with a pool that supports local languages or offers tools and services best suited to specific regional needs.
In conclusion, choosing a mining pool is a multifactorial decision that must consider the type of cryptocurrency, individual and market conditions, and personal preferences of the miner regarding risk, profitability, and stability. An informed choice can significantly increase the chances of success and satisfaction from mining, making it not only profitable but also a sustainable activity.