Understanding mining pools: A comprehensive overview
In the dynamic and complex world of cryptocurrency, mining pools play a pivotal role. For those looking to delve into cryptocurrency mining or optimize their mining efforts, understanding mining pools is essential. This comprehensive overview will explore what mining pools are, how they function, and why they are crucial for miners seeking to maximize their efficiency and earnings.
Earn more money with Headframe
Join a mining pool and get the best profitability in mining. Already more than 10,000 miners trust Headframe.
At its core, a mining pool is a collective group of cryptocurrency miners who combine their computational resources to enhance their chances of successfully mining a block. Mining cryptocurrencies, particularly major ones like Bitcoin and Ethereum, involves solving complex mathematical puzzles that require significant computational power. As individual miners, the likelihood of solving these puzzles and receiving the associated rewards can be quite low, especially with the increasing difficulty levels of mining operations. By joining a mining pool, miners effectively pool their resources, making it more probable to solve these puzzles and earn rewards.
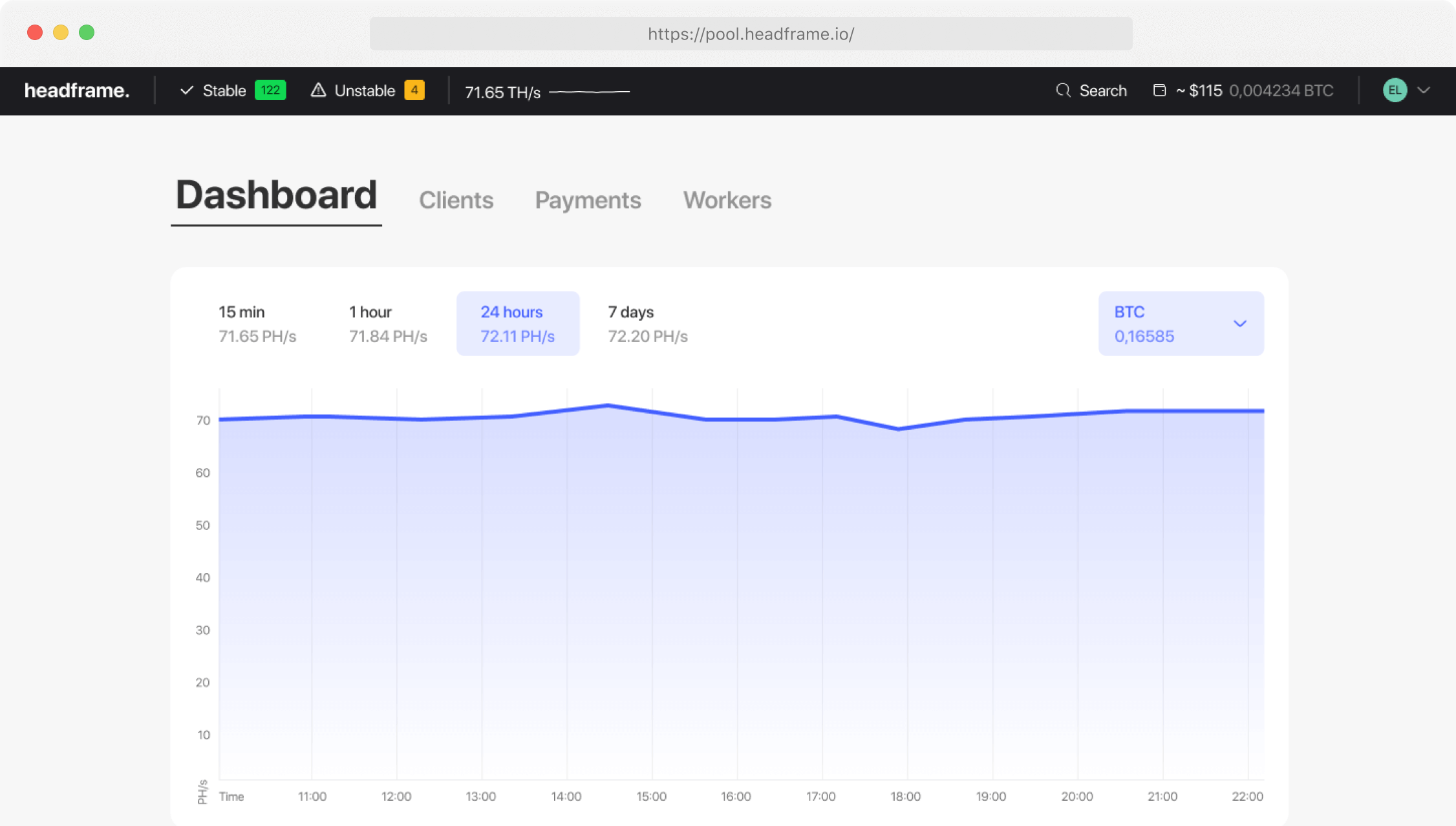
The fundamental concept behind mining pools is straightforward. Miners contribute their hash power—the computational power used in mining—to the pool. When the pool successfully mines a block, the reward is distributed among the pool members based on the amount of computational power each miner contributed. This collaborative approach leads to more consistent and frequent payouts for individual miners, as opposed to the sporadic and uncertain income from solo mining.
The operation of mining pools involves several critical components and processes. First, miners connect their mining hardware to the pool’s server. This connection allows the pool to monitor and coordinate the collective mining efforts. The pool server assigns work to each miner, ensuring that all computational resources are effectively utilized. This coordination is crucial for maintaining high efficiency and maximizing the chances of successfully mining blocks.
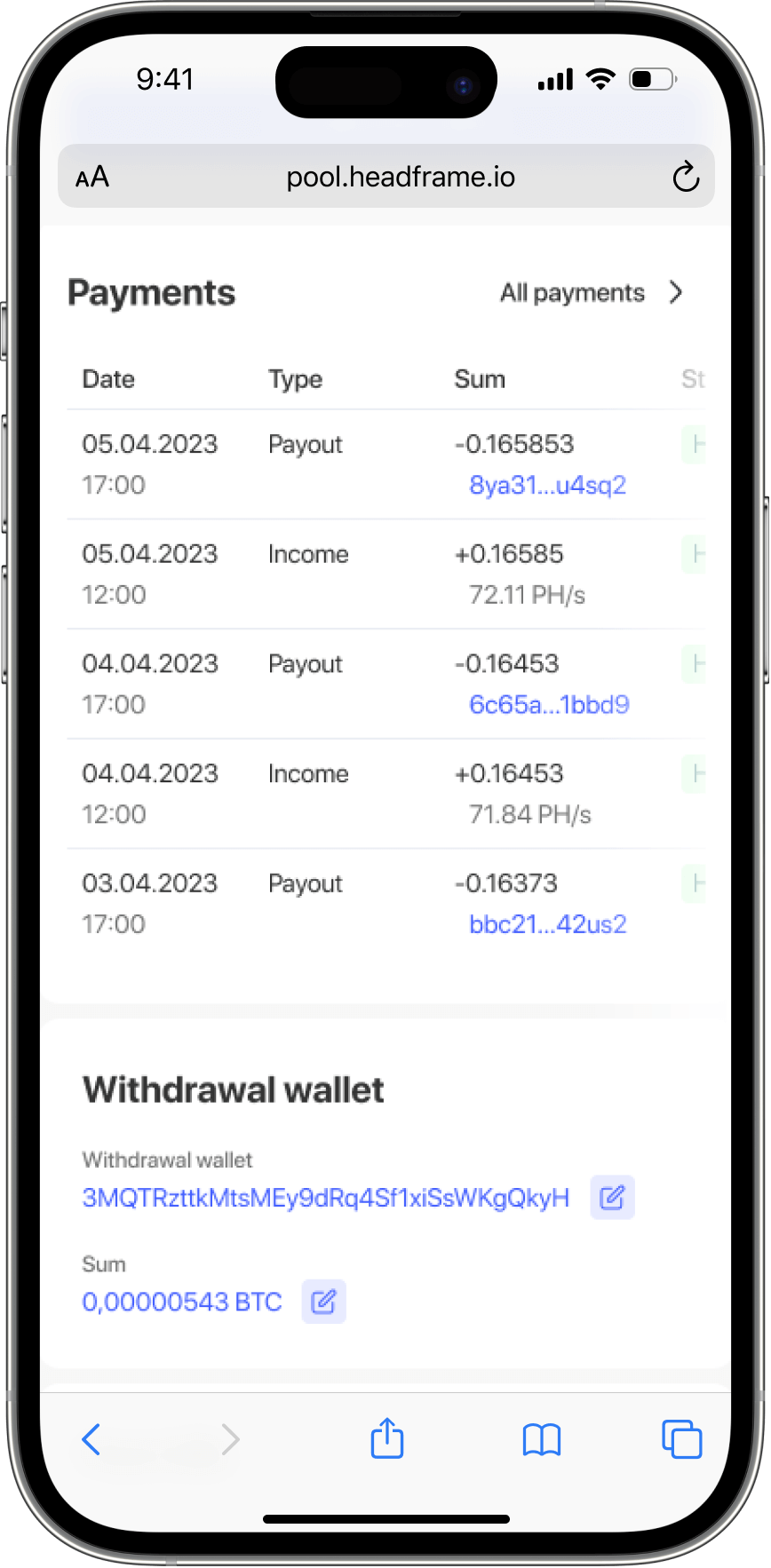
Once a block is mined, the pool verifies the solution and submits it to the cryptocurrency network. If the solution is accepted, the block is added to the blockchain, and the mining reward is credited to the pool. The pool then distributes the reward to its members based on their contributions. Different pools use various methods to calculate and distribute these rewards, including Pay Per Share (PPS), Proportional (PROP), and Pay Per Last N Shares (PPLNS).
PPS is a popular payout method where miners receive a fixed payment for each share they contribute to the pool, regardless of whether the pool finds a block. This method provides a steady and predictable income stream, which can be particularly appealing to miners seeking stability. However, PPS typically involves higher pool fees to account for the consistent payouts.
PROP is another common payout method, where rewards are distributed proportionally based on the number of shares each miner contributed during the mining of a particular block. This method can lead to higher payouts during periods of high mining activity but introduces more variability in income. PPLNS, on the other hand, calculates rewards based on the number of shares contributed during the last N shares, providing a balance between the stability of PPS and the potential higher rewards of PROP.
The choice of payout method can significantly impact a miner’s overall earnings and risk profile. Therefore, it is crucial for miners to understand the different payout methods and select a pool that aligns with their mining strategy and risk tolerance.
Beyond the basic mechanics of mining pools, several factors influence their efficiency and effectiveness. The pool’s hash rate, which represents the total computational power contributed by its members, is a key determinant of its success. A higher hash rate increases the probability of solving blocks and earning rewards. However, it also means that rewards are distributed among more members, potentially reducing individual payouts.
Pool fees are another critical consideration. Most pools charge a fee for their services, typically ranging from 1% to 3% of the mining rewards. These fees cover operational costs and fund the pool’s infrastructure and support services. While higher fees can impact overall profitability, they may be justified by the quality of services and support provided by the pool.
Security is paramount in the cryptocurrency mining landscape. Reputable mining pools implement robust security measures to protect their members’ contributions and earnings. These measures include two-factor authentication, encryption, and regular security audits. Some pools also offer additional security features, such as DDoS protection and automatic backup systems, to safeguard against potential threats.
Transparency and trust are also vital aspects of mining pools. Reliable pools provide detailed information about their operations, including fee structures, payout methods, and performance metrics. Transparency in these areas ensures that miners can make informed decisions and trust the pool to operate fairly and ethically. Reputable pools often have a proven track record of consistent and fair operations, which can be verified through user reviews and community feedback.
The geographic distribution of pool servers is another factor that can affect mining efficiency. Pools with servers strategically located across multiple regions can offer lower latency and more stable connections, improving overall mining performance. Miners should consider the pool’s server locations and choose one that minimizes latency based on their geographic location.
Customer support and community engagement are additional considerations. Effective customer support can help miners resolve issues quickly and optimize their mining operations. Pools with active community forums and social media presence provide valuable resources for miners to exchange knowledge, tips, and best practices.
While mining pools offer numerous benefits, they also present certain challenges and risks. The centralization of mining power within large pools can raise concerns about the security and integrity of the blockchain. If a single pool controls more than 50% of the network’s hash rate, it could theoretically execute a 51% attack, potentially manipulating transactions and undermining trust in the cryptocurrency. Although such scenarios are rare, they highlight the importance of decentralization in maintaining the blockchain’s security.
Moreover, the choice of a mining pool should be aligned with the miner’s specific goals and resources. Smaller pools may offer higher individual payouts but with less frequency, while larger pools provide more consistent payouts with potentially lower individual rewards. Miners must carefully evaluate their options and select a pool that best suits their needs and preferences.
In conclusion, understanding mining pools is crucial for anyone involved in cryptocurrency mining. These pools enhance the efficiency and profitability of mining operations by pooling resources and providing more consistent rewards. However, miners must consider various factors, including payout methods, fees, security, transparency, server distribution, and support, to choose the right pool. By making informed decisions and staying updated on the latest developments in the mining landscape, miners can optimize their efforts and achieve greater success in the competitive world of cryptocurrency mining.