Joining a mining pool: Legal and regulatory considerations
Cryptocurrency mining, particularly through mining pools, has become a significant industry worldwide. As this sector grows, it is increasingly subject to legal and regulatory scrutiny. Understanding the legal and regulatory considerations for mining pools is essential for ensuring compliance and mitigating potential risks. This guide explores the key legal aspects and offers insights to help mining pool operators and participants stay informed and compliant.
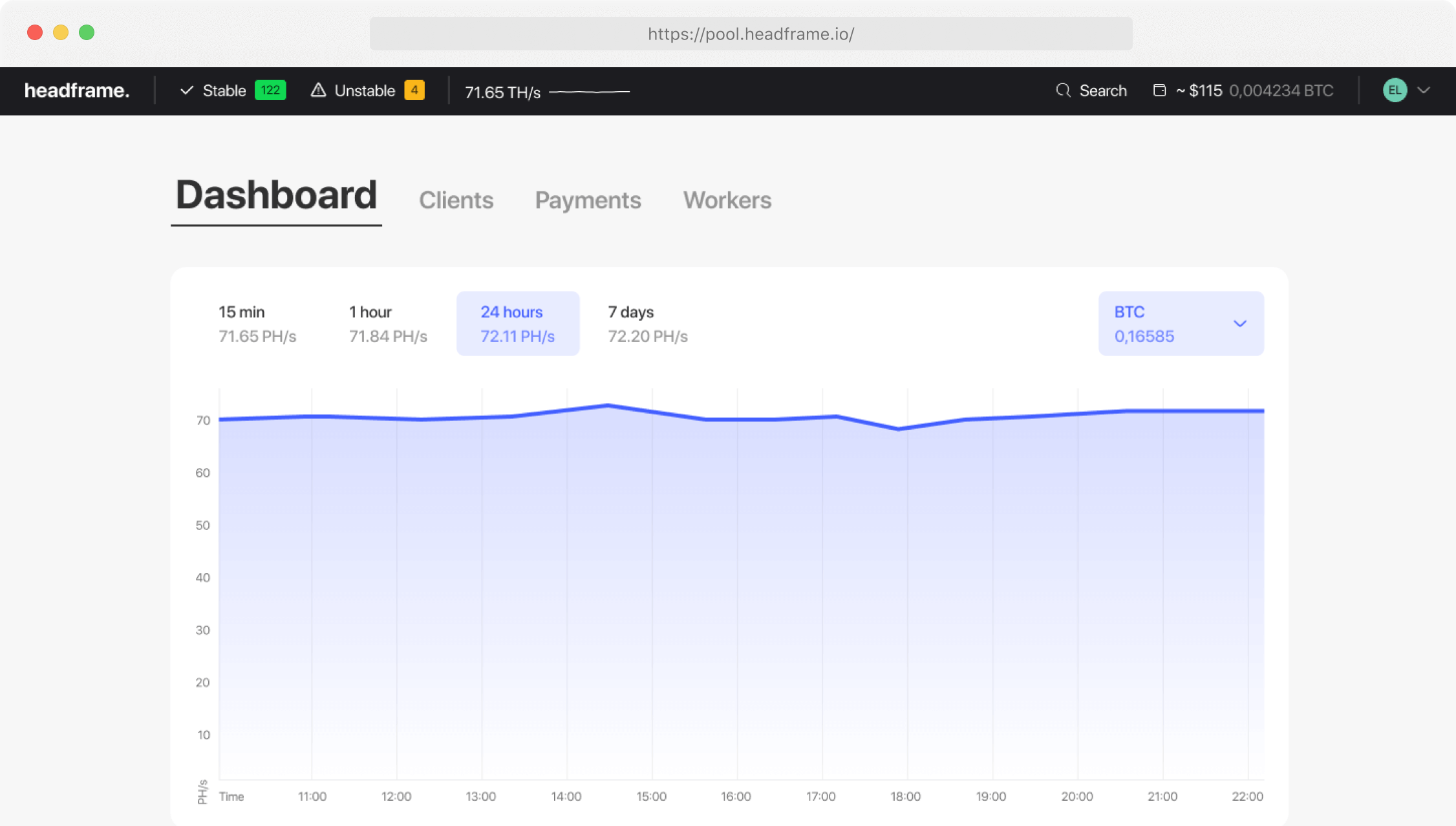
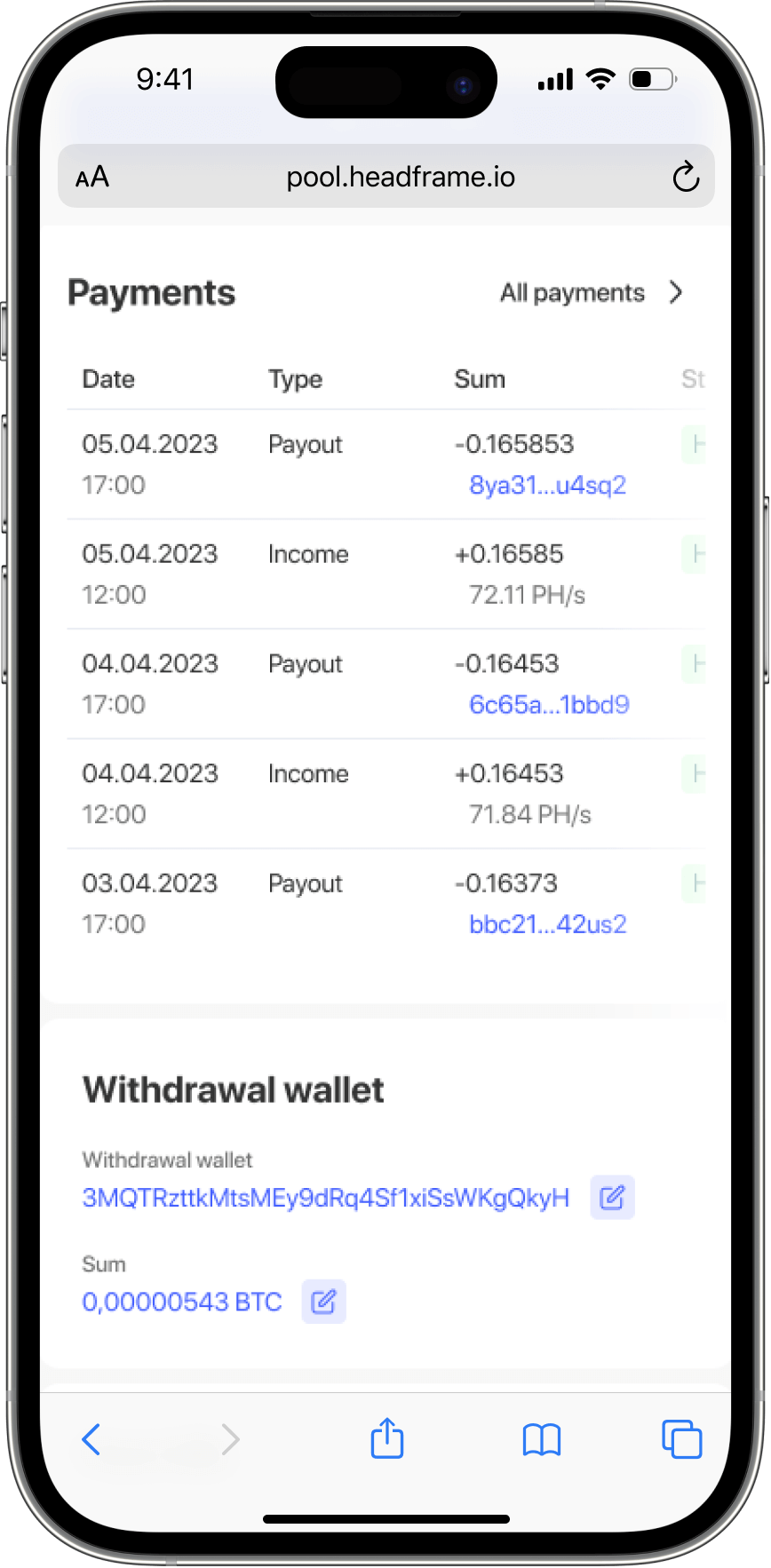
Earn more money with Headframe
Join a mining pool and get the best profitability in mining. Already more than 10,000 miners trust Headframe.
One of the primary legal considerations for mining pools is the regulatory environment in which they operate. Different countries have varying regulations regarding cryptocurrency mining, and these can impact the legality and operation of mining pools. Some jurisdictions have embraced cryptocurrency mining and established clear regulatory frameworks, while others have imposed strict restrictions or outright bans. It is crucial for mining pool operators and participants to understand the regulatory landscape in their respective regions and ensure that their activities comply with local laws.
In regions where cryptocurrency mining is permitted, regulatory requirements often include licensing and registration. Mining pool operators may need to obtain specific licenses to operate legally, depending on the jurisdiction. These licenses can involve rigorous application processes and ongoing compliance obligations, such as regular reporting and audits. Failing to obtain the necessary licenses can result in significant penalties, including fines and shutdown orders. Therefore, it is essential for mining pool operators to thoroughly research and comply with licensing requirements in their operating regions.
Another critical regulatory consideration is taxation. The tax treatment of cryptocurrency mining can vary widely between jurisdictions. In some regions, mining rewards are considered taxable income, and miners must report their earnings and pay income tax accordingly. Additionally, the sale or exchange of mined cryptocurrency can trigger capital gains tax obligations. Mining pool operators and participants must understand their tax liabilities and maintain accurate records of their mining activities to ensure compliance with tax laws. Consulting with a tax professional who specializes in cryptocurrency can help navigate these complex tax issues.
Anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CTF) regulations are also significant concerns for mining pools. Given the pseudonymous nature of cryptocurrencies, regulators are increasingly focused on preventing their use for illicit activities. Many jurisdictions require cryptocurrency businesses, including mining pools, to implement robust AML and CTF measures. These measures typically include customer due diligence (CDD) procedures, such as verifying the identities of participants, monitoring transactions for suspicious activity, and reporting any suspicious transactions to relevant authorities. Mining pool operators must establish comprehensive AML and CTF programs to comply with these regulations and reduce the risk of legal issues.
Privacy and data protection regulations are another important aspect of operating a mining pool. Mining pool operators collect and process personal data from their participants, including identification information, payment details, and transaction records. As such, they are subject to data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. These laws require operators to implement appropriate safeguards to protect personal data, obtain consent for data processing, and provide individuals with rights over their data, such as the right to access, rectify, and delete their information. Non-compliance with data protection regulations can result in severe penalties, making it essential for mining pool operators to adhere to these legal requirements.
The environmental impact of cryptocurrency mining is another area of regulatory concern. Mining operations, particularly those involving energy-intensive proof-of-work (PoW) algorithms, consume significant amounts of electricity and contribute to carbon emissions. As a result, some jurisdictions have introduced regulations aimed at reducing the environmental impact of mining. These regulations can include restrictions on energy consumption, requirements for using renewable energy sources, and penalties for excessive carbon emissions. Mining pool operators should be aware of any environmental regulations in their regions and take steps to minimize their environmental footprint, such as adopting energy-efficient practices and exploring renewable energy options.
Intellectual property (IP) rights are also relevant to mining pools. The development and use of proprietary mining software, algorithms, and technologies can give rise to IP issues. Mining pool operators should ensure that they have the necessary rights and licenses to use any third-party software or technology and take steps to protect their own IP. This can involve registering patents, trademarks, and copyrights, as well as implementing measures to prevent unauthorized use or infringement of their IP.
Securities regulations are another area of potential legal concern for mining pools. In some jurisdictions, certain activities related to cryptocurrency mining and the issuance of tokens can be considered securities offerings, subject to securities laws. This can include initial coin offerings (ICOs) and other fundraising activities that involve the sale of tokens or other digital assets. Mining pool operators should be cautious of any activities that could be interpreted as securities offerings and seek legal advice to ensure compliance with securities regulations.
Consumer protection laws are also applicable to mining pools, particularly those that offer services to individual miners. These laws are designed to protect consumers from unfair practices and ensure transparency and fairness in business operations. Mining pool operators must provide clear and accurate information about their services, including fees, payout methods, and potential risks. They should also establish mechanisms for resolving disputes and addressing complaints from participants. Compliance with consumer protection laws helps build trust and credibility with participants and reduces the risk of legal disputes.
Staying informed about legal and regulatory developments is crucial for mining pool operators and participants. The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrency mining is constantly evolving, with new laws and regulations being introduced regularly. Keeping up to date with these changes can help ensure ongoing compliance and mitigate legal risks. This can involve subscribing to industry news sources, participating in industry associations, and consulting with legal professionals who specialize in cryptocurrency and blockchain technology.
In conclusion, operating and participating in mining pools involves navigating a complex web of legal and regulatory considerations. Understanding and complying with licensing, taxation, AML/CTF, privacy, environmental, intellectual property, securities, and consumer protection regulations is essential for mitigating legal risks and ensuring the long-term success of mining operations. By staying informed about regulatory developments and seeking professional legal advice, mining pool operators and participants can effectively manage their legal obligations and contribute to a sustainable and compliant cryptocurrency mining ecosystem.